Fast delivery
Global supplier
Innovative solutions
Innovations in Building Materials: A Comprehensive Look at New FRP Angle Steel
Jul 13,2025
Innovations in Building Materials: Spotlight on New FRP Angle Steel
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to FRP Angle Steel
- 2. What is Fiber Reinforced Polymer (FRP)?
- 3. Benefits of Using FRP Angle Steel in Construction
- 4. Applications of FRP Angle Steel
- 5. Comparison of FRP Angle Steel with Traditional Steel
- 6. Case Studies of FRP Angle Steel Implementation
- 7. The Future of FRP Materials in Building
- 8. Conclusion
- 9. FAQs about FRP Angle Steel
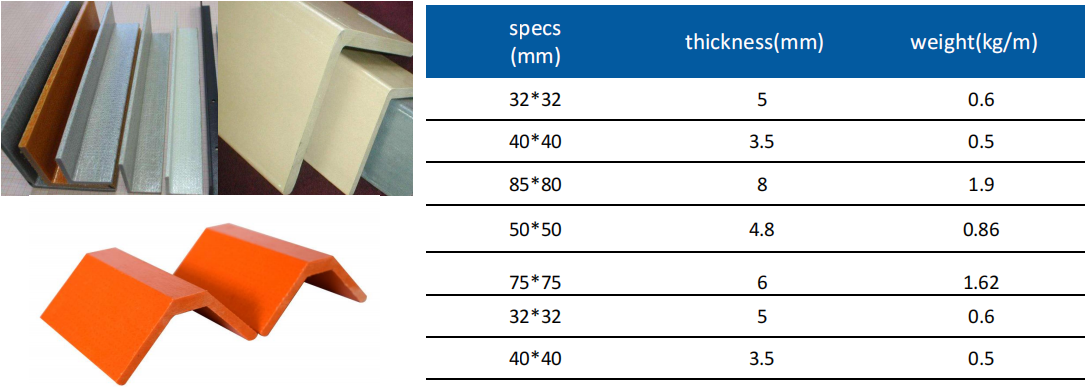
1. Introduction to FRP Angle Steel
As the construction industry evolves, so do the materials that underpin our infrastructure. **Fiber Reinforced Polymer (FRP)** angle steel represents one of the most significant innovations in building materials, offering numerous benefits that traditional materials cannot match. In this article, we will explore the characteristics, benefits, and applications of FRP angle steel, along with its impact on modern construction practices.
2. What is Fiber Reinforced Polymer (FRP)?
Fiber Reinforced Polymer (FRP) is a composite material made of a polymer matrix reinforced with fibers. The fibers are typically made from glass, carbon, or aramid, providing high strength and low weight. **FRP is known for its remarkable properties**, which include:
- **High strength-to-weight ratio**: This allows for lighter structures without compromising strength.
- **Corrosion resistance**: Unlike traditional steel, FRP does not rust, making it ideal for harsh environments.
- **Thermal and electrical insulation**: FRP provides excellent insulation properties, useful in various applications.
3. Benefits of Using FRP Angle Steel in Construction
FRP angle steel has emerged as a game-changer in the construction sector due to its many advantages:
3.1 Lightweight Yet Strong
Despite its lightweight nature, FRP angle steel possesses impressive strength. This characteristic not only eases transportation and installation but also reduces overall project costs.
3.2 Durability and Longevity
One of the most appealing aspects of FRP angle steel is its durability. Resistant to various environmental factors, including moisture, chemicals, and UV radiation, FRP structures can last significantly longer than their steel counterparts.
3.3 Cost-Effectiveness Over Time
While the initial investment in FRP angle steel may be higher, its long-term savings on maintenance and replacement costs make it a cost-effective choice. Reduced corrosion means less frequent repairs and a longer service life.
3.4 Enhanced Aesthetic Appeal
FRP angle steel can be manufactured in various colors and finishes, allowing for greater aesthetic flexibility in design. This versatility is essential in modern architecture, which often emphasizes visual appeal.
4. Applications of FRP Angle Steel
The applications of FRP angle steel are expansive, spanning several sectors within the construction industry:
4.1 Infrastructure Development
FRP angle steel is widely used in the construction of bridges, roads, and tunnels. Its lightweight and strong properties make it an excellent choice for structural components that must endure heavy loads.
4.2 Marine and Coastal Structures
In marine environments, where exposure to saltwater and moisture is a concern, FRP angle steel proves to be a superior material. It resists corrosion, ensuring longevity and reliability in docks, piers, and other coastal infrastructures.
4.3 Building Construction
From commercial buildings to residential projects, FRP angle steel is increasingly utilized in framing and support systems. Its combination of strength and weight makes it ideal for various structural applications.
4.4 Industrial Applications
Industries that require robust and durable materials, such as chemical processing and food production, benefit from the use of FRP angle steel. Its resistance to chemicals and easy cleaning properties are significant advantages.
5. Comparison of FRP Angle Steel with Traditional Steel
Understanding how FRP angle steel compares to traditional steel is crucial for making informed decisions in construction projects:
5.1 Weight and Strength
While traditional steel is heavy, requiring robust foundations, FRP angle steel’s lightweight nature allows for easier handling and transportation, resulting in lower overall project costs.
5.2 Corrosion Resistance
Traditional steel requires protective coatings to resist rust, necessitating ongoing maintenance. In contrast, FRP angle steel’s inherent corrosion resistance reduces long-term maintenance requirements and costs.
5.3 Thermal Properties
FRP angle steel offers superior thermal insulation compared to traditional steel, which can conduct heat and cold. This property leads to improved energy efficiency in buildings, reducing heating and cooling costs.
5.4 Life Cycle Cost Analysis
Initial costs aside, life cycle assessments show that FRP angle steel often proves to be more cost-effective over time due to its durability and reduced maintenance needs.
6. Case Studies of FRP Angle Steel Implementation
To illustrate the effectiveness of FRP angle steel, we present several case studies that highlight its successful use in real-world applications.
6.1 Case Study: Coastal Bridge Construction
In a recent project involving the construction of a coastal bridge, FRP angle steel was chosen for its ability to withstand harsh marine conditions. The bridge was completed ahead of schedule, and the durability of the materials used has significantly reduced maintenance costs.
6.2 Case Study: Industrial Facility Expansion
An industrial facility expanded its production capacity using FRP angle steel for its new structures. The lightweight and non-corrosive nature of the material allowed for faster installation and reduced downtime during construction.
7. The Future of FRP Materials in Building
As technology continues to advance, the future of FRP materials looks promising. Ongoing research and development are focused on enhancing the properties of FRP, making it even more applicable across various sectors.
7.1 Innovations in Manufacturing
New manufacturing techniques are emerging that may further lower costs and improve the performance of FRP angle steel. These innovations could lead to wider adoption in construction projects globally.
7.2 Sustainable Building Practices
With growing emphasis on sustainability, FRP materials are becoming a focal point in green building initiatives. Their longevity and recyclability align with modern environmental standards.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, **FRP angle steel represents a significant advancement in building materials**, offering numerous benefits over traditional steel. Its lightweight, durable, and corrosion-resistant properties make it an excellent choice for a wide range of applications, from infrastructure to industrial settings. As the construction industry continues to evolve, the adoption of materials like FRP angle steel will play a crucial role in shaping the future of building practices.
9. FAQs about FRP Angle Steel
9.1 What are the main advantages of FRP angle steel?
FRP angle steel offers a lightweight alternative to traditional steel, enhanced durability, corrosion resistance, and reduced maintenance costs.
9.2 Can FRP angle steel be used in high-temperature environments?
Yes, FRP angle steel can withstand various temperatures; however, specific applications may require specialized formulations.
9.3 How does FRP angle steel compare in cost to traditional steel?
While the upfront cost of FRP angle steel may be higher, its long-term savings on maintenance and replacement make it a cost-effective option.
9.4 Is FRP angle steel recyclable?
Yes, FRP materials can be recycled, making them an environmentally friendly choice for construction.
9.5 Where can I find suppliers of FRP angle steel?
Many construction material suppliers now stock FRP angle steel; it is advisable to research local suppliers or manufacturers for availability.
In the face of ongoing innovations, **FRP angle steel is poised to reshape the landscape of building materials**, making it an essential option for contemporary construction projects.
Contact Us
Tel:
+86017717930013 +86013621742959
Email:
Address:
No.99 Denggao Road, Motou Town, Rugao City, Jiangsu Province, China.